Chemistry of Blood Groups
Chemistry of Blood Groups
 |
| types of blood groups |
International Society of Blood Transfusion has recently recognized 33 blood group systems. Apart from ABO and Rhesus system, many other types of antigens have been noticed on the red cell membranes. Blood grouping and cross-matching is one of the few important tests that the anesthesiologist orders during the perioperative period. Hence, a proper understanding of the blood group system, their clinical significance, typing and cross-matching tests, and current perspective are of paramount importance to prevent transfusion-related complications It is firmly established that ABO and rhesus (Rh) genes and phenotypes remain the most significant blood factor in clinical applications, it also proves to be a valuable assets for determining human migration patterns and origins. To determine the prevalence of ABO and Rh blood groups based on the antigenic presence on the surface of red blood cells concerning gender and calculate the allele frequency of the blood groups. Globally, approximately 700 type red cell antigens have been identified till now. ABO and Rh blood groups play an important role in the process of blood transfusion, resolving certain medico-legal issues, parental testing, and various genetic studies.
Introduction
Platelets:
Platelets, or thrombocytes, are cell fragments without nuclei that work with blood clotting chemicals at the site of wounds. They do this by adhering to the walls of blood vessels, thereby plugging the rupture in the vascular wall. They also can release coagulating chemicals that cause clots to form in the blood that can plug up xiinarrowed blood vessels.
 |
| erythrocyte
(left), thrombocyte (center), and leukocyte (right) |
Plasma:
is the moderately clear, yellow-colored water (92+%), sugar, fat, protein, and salt arrangement which conveys the red cells, white cells, and platelets. Regularly, 55% of our blood's volume is comprised of plasma. As the heart siphons blood to cells all through the body, plasma carries sustenance to them and eliminates the byproducts of digestion. Plasma additionally contains blood coagulating factors, sugars, lipids, vitamins,minerals, chemicals, compounds, antibodies, and different proteins
Introduction to Human Factors Blood Groups:
The most notable and medicinally significant blood classifications are in the ABO gathering. They were found in 1900 and 1901 at the University of Vienna by Karl Landsteiner during the time spent attempting to realize why blood bondings here and there cause demise and at different occasions save a patient.(Schwarz and Dorner, 2003)
The ABO Blood bunch System:
All people and numerous different primates can be composed for the ABO blood gathering. There are four chief sorts: A, B, AB, and O. there are two antigens and two antibodies that are generally answerable for the ABO types. The particular blend of these four segments decides a person's sort much of the time. The table beneath shows the potential changes of antigens and antibodies with the comparing ABO type ("yes" demonstrates the presence of a part and "no" demonstrates its nonappearance in the blood of a person).
 |
Fig.2.ABO Blood group |
It is simple and reasonable to decide a person's ABO type from a couple of drops of blood. A serum containing hostile to An antibodies is blended in with a portion of the blood. Another serum with hostile to B antibodies is blended in with the excess example. Regardless of whether agglutination happens in either test shows the ABO type. It is a straightforward interaction of end of the prospects. For example, if a person's blood test is agglutinated by the counter An immune response, yet not the counter B neutralizer, it implies that the An antigen is available however not the B antigen. Hence, the blood classification is A.
Genetic Inheritance Patterns:
Exploration completed in Heidelberg, Germany by Ludwik Hirszfeld and Emil von Dungeon in 1910 and 1911 demonstrated that the ABO blood classifications are acquired. We currently realize that they are dictated by qualities on chromosome 9, and they don't change because of natural impacts during life. A person's ABO type results from the legacy of 1 of 3 alleles (A, B, or O) from each parent. The potential results are appeared beneath.
|
Parent Alleles |
A |
B |
O |
|
A |
AA |
AB |
AO |
|
B |
AB |
BB |
BO |
|
O |
AO |
BO |
OO |
parent are in the top row and the
alleles of the other are in the left
column. Offspring genotypes
are shown in black. Phenotypes
are red.
GENES ENCODING GLYCOSYLTRANSFERASES INVOLVED IN SYNTHESIS OF ABO BLOOD GROUP CARBOHYDRATE ANTIGEN STRUCTURES IN HUMANS.
The single ABO quality locus in people has three allele's sorts A, B, and O. Loci An and B encode two distinctive dynamic glycosyltransferases that catalyze the biosynthesis of An and B terminal sugar antigen groupings, utilizing O antigen carb structure as an antecedent. The O locus is encoding nonfunctional catalysts. Both An and B chemicals have a place with the glycosyltransferase family numbered as 6, as per the HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee which is the solitary overall position that allocates normalized terminology to human qualities. The human ABO quality is situated on chromosome 9 position. The cytogenetic band is named. The genomic organizes are (GRCh38). This quality has a place with the glycosyltransferase family 6. The ABO quality has 7 exons with exon 7 having the biggest coding grouping. (Seto et al., 1995)The coding succession has more than 18-kilo base pairsand exons size range beA B C. ABO blood bunch antigen glycan groupings. ABO blood bunch antigen glycan arrangements are introduced in shortened substance letter structure, synthetic primary structure, and schematic structure as per, Gal: galactose; Fuc: fucose; GalNAc: N-acetyl galactosamine.ABO quality construction. Schematic introduction of ABO quality chromosomal area and exons positions encoding glycosyltransferase An and B.
Historical Background:
It was not until the year 1900, when Karl Landsteiner at the University of Vienna, found why some blood bondings were fruitful while others could be dangerous. Landsteiner found the ABO blood bunch framework by blending the red cells and serum of every one of his staff. He showed that the serum of certain individuals agglutinated the red cells of others. From these early examinations, he recognized three sorts, called A, B and (C was later to be re-named O for the German "Ohne", signifying "without", or "Zero", "invalid" in English). The fourth less regular blood bunch AB was found a year later. In 1930, Landsteiner got the Nobel Prize in physiology and medication for his work.(Seto et al., 1995)The quality that decides the human ABO blood classification is situated on chromosome 9 and is called ABO glycosyltransferase. The ABO locus has three primary allelic structures: A, B, and O, as referenced above and every one of them is answerable for the creation of its glycoprotein. As examinations have exhibited on monkeys, human blood bunches are exceptionally old hereditary pointers that have developed more than a few million years. In view of the essential races theory, it was believed that in the three significant races of man, blood bunches An in Europe, B in Asian, lastly O in South America have been arisen and progressively because of the movement and blending of the races, turned into the current circumstance. However, we realize that in every landmass, the confined populaces are seen that have totally extraordinary blood gatherings. For instance, there is a generally high pervasiveness of blood bunch O in Siberian occupants; likewise this blood bunch is basic in certain regions.
Percentage of blood groups in monkeys (collected by Kramps 1960)
 |
| blood cells |
The mother won't have manifestations from isoimmunization however for the infant indications can go from gentle to perilous. Indeed, even mellow, the contrariness obliterates the red platelets without demonstrating different impacts. At the point when the cycle is sufficiently extreme, the child can turn out to be exceptionally pale and, now and again may pass on. After birth, the child's skin and whites of the eyes will seem yellow (jaundice) and the infant will have low muscle tone (hypotonia) and torpidity.
How is isoimmunization diagnosed?
Ladies in danger for isoimmunization can be distinguished at pre-birth visits with tests that measure blood classification, Rh type, and immune response screening. Periodically the particular contradiction is analyzed before birth through amniocentesis. On the off chance that isoimmunization is analyzed, we screen the seriousness of the infant's sickliness using ultrasound. After birth, there may likewise be a positive perusing on a blood test called Coombs, higher-than-ordinary degrees of bilirubin from blood tests from the child's umbilical line, and indications of red platelet obliteration in the baby's blood.
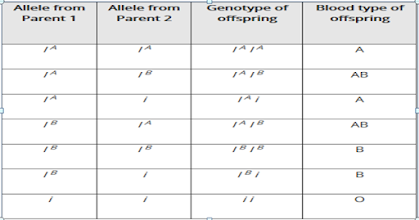 |
Fig.4. the Genetic Basis of Blood Grouping in Human
Population.
When recognized as having Rh-negative blood classification, the pregnant or potentially recently conveyed mother can be given RhoGAM (Rh-resistant globulin).
What is the treatment for
isoimmunization?
Glycoproteins:
Film bound glycoproteins partake in a wide scope of cell marvels, including cell acknowledgment, cell surface antigenicity, and so forth In the glycoproteins, most of the particle comprise of proteins; they have at least one oligosaccharides connected to a protein, and they generally are fanned and don't have sequential rehashes, so they are wealthy in data, shaping profoundly explicit destinations for acknowledgment and high-liking restricting by other proteins.
Glycolipids:
Glycolipids are film lipids in which the hydrophilic head bunches are oligosaccharides.O-N-acetylgalactosamine (O-GalNAc)The expansion of N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) to a serine or threonine happens in the Golgi mechanical assembly, after the protein has been folded.The measure is performed by chemicals known as GalNAc transferases (GALNTs), of which there are 20 distinctive types.The starting O-GalNAc design can be altered by the expansion of different sugars, or different mixtures, for example, methyl and acetyl groups.(Roberts, 1988) Thrombospondin ties to the secluded glycolipid, and the glycolipid and an immunizer to this construction repress cell spreading on thrombospondin substrates. Consequently, the presence of glycoconjugates with terminal nonreducing glucuronosyl 3-sulfate associates with melanoma cell spreading on thrombospondin, while articulation of heparan sulfate proteoglycans that tight spot thrombospondin doesn't. (Miura et al., 1999) The saccharides that are connected to the polar head bunches outwardly of the cell are the ligand segments of glycolipids, and are moreover polar, permitting them to be dissolvable in the fluid climate encompassing the cell.
 |
Fig.5.O-GalNAc core
structures; Core 1, Core 2, and poly-N-acetyllactosamine structures.
The biosynthesis of
N-linked glycan’s occurs via 3 major steps:
1.
Synthesis of dolichol-linked precursor
oligosaccharide
2.
En bloc transfer of precursor
oligosaccharide to protein
3.
Processing of the oligosaccharide
 |
Fig.6.Biosynthesis
of N-Linked glycoprotein:
|
The synthesis of glycan starts in the
endoplasmic reticulum, continues in the Golgi, and ends at the plasma membrane,
where the N-linked glycoproteins are either secreted or becomes embedded in the
plasma membrane. |
Biosynthesis of glycosphingolipids:
 |
| test to find blood group |
humanoid primates to communicate ABH antigens on their red cells. ABH or ABH-like determinants have likewise been recognized in plants and microorganisms, yet these determinants are not being talked about here.
ABO(H) System:
The characters characterized in the ABO(H) framework are dependent upon severe hereditary control and accordingly are acquired as basic Mendelian prevailing characters. Event and conveyance of ABH specificities are constrained by three autonomous however firmly interrelated quality systems.The ABO Gene The three alleles A B, and 0 of this quality locus represent the four fundamental blood gatherings, A, B, AB, and O. The alleles An and B control the arrangement of An and B explicitness on erythrocytes and in emissions, though the dormant 0 allele doesn't offer ascent to any blood bunch character. The connection between ABO genotype and noticed erythrocyte aggregate is introduced in.The dominant part of An and B subgroups characterized to date are constrained by variations of An and Bgenes. The ABO locus has been restricted on chromosome 9, position. The Hh Gene The blood bunch H character is found on erythrocytes and in discharges of blood bunch 0 people and has subsequently been viewed as the result of the 0 gene.(Schenkel-Brunner, 2000) H determinants, nonetheless, are additionally present, however not in amount, in A, B, and AB subjects. Since people of genotypes M BB and AB come up short on the 0 qualities, Watkins and Morgan inferred that this particularity should be the result of a free quality, which they assigned HH substance addresses the forerunner which, affected by qualities An and B, is changed over into blood bunch An or B substance, separately. Since the latent 0 allele not the slightest bit modifies H substance, the presence of unaltered H determinants is trademark for 0 people. There is besides a proportional relationship.
1.
ABH Antigens on Red Cells and in Plasma:
ABO(H) System:
 |
| blood group experiments |
ABH Secretion:
1.
Test for Secretor Status (Inhibition Test)
To test for secretor status, a restraint or balance test is finished utilizing spit. The rule of the test is that if ABH antigens are available in a solvent structure in a liquid (e.g., spit) they will kill their comparing antibodies and the antibodies can not, at this point agglutinate red cells having similar antigens. (Note: Secretor status testing is only from time to time, if at any time, done today because of the approach of more strong monoclonal composing reagents and DNA technology.)(Raza et al., 1991)
5.2Antisera& Lectins: Antisera are utilized to figure out which antigens are on the red cells. The test utilizing antisera and the patient's red cells is known as the front cell gathering. The antisera utilized in the front gathering are acquired from plasmapheresis of benefactors invigorated with solvent antigens (A substance from pig mucosa and B substance from horse mucosa). On the other hand, monoclonal antisera can be set up from refined cell lines.
1.
anti-A (from group B people)
The
government regulations specify that anti-A be colored blue as a quality control
(QC) measure.
2.
anti-B (from group A people)
The
government regulations specify that anti-B be colored yellow as a QC measure.
3.
anti-A,B (from group O people)
Against A,B is lackluster (no color is added). Utilization of against A,B shifts from lab to lab. A few labs use it for all ABO gathering, and some utilization it to affirm bunch O composing. Other blood donation centers use it specifically as follows:to bunch babies (whose converse gathering is inconsistent and can't be utilized as a mind the front cell group).whenever errors happen between the front and opposite gathering, particularly disparities because of powerless or missing antigens. Note: monoclonal enemy of A,B is greater at identifying powerless subgroups than is human enemy of A,B.when exploring suspected hemolytic bonding responses
Main uses of anti-A,B:
1.
To confirm the front cell group in newborns.
2.
To help resolve ABO discrepancies.
Monoclonal
Reagents: murine (mouse) monoclonal anti-A and anti-B reagents prepared using
hybridoma technology are available as alternatives to human antisera. These
monoclonal antisera are very specific and very potent (sensitive). They are
useful when investigating both weak and extra antigens, e.g., weak subgroups of
A or acquired B phenomenon.
ABH Substances of erythrocytes:
The commitment of blood-bunch dynamic glycolipids and glycoproteins to the blood-bunch ABHcharacter of human erythrocytes was explored. For that reason the blood-bunch H locales of human O cells were changed over in vitro into bunch A destinations by move of alpha-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine deposits with the guide of the blood-bunch A quality ward alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminyl transferase arranged from human A1 plasma. Upon the segment of the red cell films among water and natural dissolvable, about 5% of the name was found in the natural stage and about 20% in the water stage, in this way mirroring the appropriation of blood-bunch antigenic locales between glycosphingolipids with short carb chains and polyglycosylceramides, individually. The way that about 70% of the radioactivity remained firmly bound to the layers and must be delivered by treatment with pronase gave great proof that the greater part of blood-bunch H determinants is bound to glycoprotein material. Following these outcomes it would thus be able to be accepted that blood-bunch ABH action of human erythrocytes is resolved specially by bunch explicit glycoproteins instead of glycolipids.
Secreted Blood group substances (Mucins):
For the two sorts of ulcers, the assessed hazard among non-secretors was comparable for blood bunch O and the other blood gatherings and the outcomes propose that the particular dangers related with blood bunch O and with non-emission duplicate each other. It is presumed that the systems by which blood bunch O and non-discharge influence the danger of building up a gastric or duodenal ulcer are identified with each other; however that they don't rely upon the presence of the blood bunch substances in the secretions.(Gibbons, 1959).
Distribution and examination of secretor status pervasiveness in people ABH antigens are available on platelets from people of the relating red cell aggregate, yet the degree to which these antigens are inborn or adsorbed stays unclear. To assess platelets for inherent H substance, an IgM mouse monoclonal immunizer against type 2H chain (the characteristic H structure found on erythrocytes) was named with 125I and brooded with platelets from contributors of various ABO type.The counter acting agent indicated portion reaction immersion bends, and restricting to platelets resembled that of the red cell ABO type, with O more noteworthy than B more prominent than A1 more prominent than A1B more prominent Oh cells, giving a solitary factor change F of 190 (P under .0005). Aloof adsorption of An antigens by platelets has been recently detailed. Human IgG against An or hostile to B was added to the platelets. The measure of counter acting agent bound was resolved with a 125I-named mouse monoclonal enemy of human IgG. When hatched for 96 hours in gathering O plasma, bunch A1 platelets indicated a 45% to half diminish in restricting of hostile to A. There was no huge change in the degree of type 2H antigen on these platelets during a similar brooding period. Gathering O platelets hatched in An or B plasmas quickly obtained the antigens, however whenever got back to their unique plasma, 95% of this inactively adsorbed antigen eluted off inside 18 hours. The greatest take-up of An and B substances was impacted by the Lewis and secretor sort of giver plasma. Our current investigation exhibits that ABH antigens on platelets comprise of type 2H chains, which are probably characteristic as when found on red cells, and of latently adsorbed ABH structures, which apparently type 1H chains.
Human milk oligosaccharides (HMO) :
are examined to assume a significant part in a baby's turn of events. Lewis blood bunch epitopes, specifically, appear to amazingly add to the valuable impacts of HMO. In such manner, enormous scope useful human examinations could give proof of the assortment of results from in vitro examinations, albeit expanding the sum and intricacy of test and information handling.Free lactose-determined oligosaccharides in human milk (HMO)are present at focuses going roughly from 10 to 20 g/L; henceforth, a few grams of these extraordinary segments go through the bosom took care of baby's gut every day (1–3). Different wellbeing defensive activities have been found from in vitro examinations, i.e., prebiotic, hostile to infective, or safe impacts which may mostly be related with the presence of fucosylated oligosaccharide structures. Those are controlled by the declaration of the secretor (Se) and Lewis (Le) qualities in the mammary organ.
Biosynthesis of neutral complex human milk oligosaccharides (HMO).
Historical Distribution of ABH Blood group into Tissues:
 |
| chenistry of blood groups |
Rh Blood group System:
Genetics:
This is a Punnett square for Rh
factor inheritance. It’s controlled by two genes, where Rh positive is
dominant. This square specifically shows two heterozygous Rh-positive parents
and the possible genotypes/phenotypes the offspring could have.






Comments
Post a Comment